Magnetite is a ferromagnetic mineral composed of iron oxide (Fe3O4), widely recognized as a high-quality iron ore due to its high iron content (up to 72.4%) and strong magnetic susceptibility. As a core raw material for the steelmaking industry, raw magnetite ore often coexists with gangue minerals (quartz, feldspar, mica) and associated minerals (hematite, sulfide, apatite) that reduce its industrial value. A professional magnetite beneficiation process—centered on magnetic separation technology—is essential to separate impurities, upgrade iron grade, and meet strict industrial standards. Our custom magnetite processing solution is tailored to ore properties (grade, particle size, associated mineral content) and production capacity, delivering high-grade magnetite concentrate that maximizes steelmaking efficiency and reduces costs.
Core Beneficiation Processes of Magnetite Ore
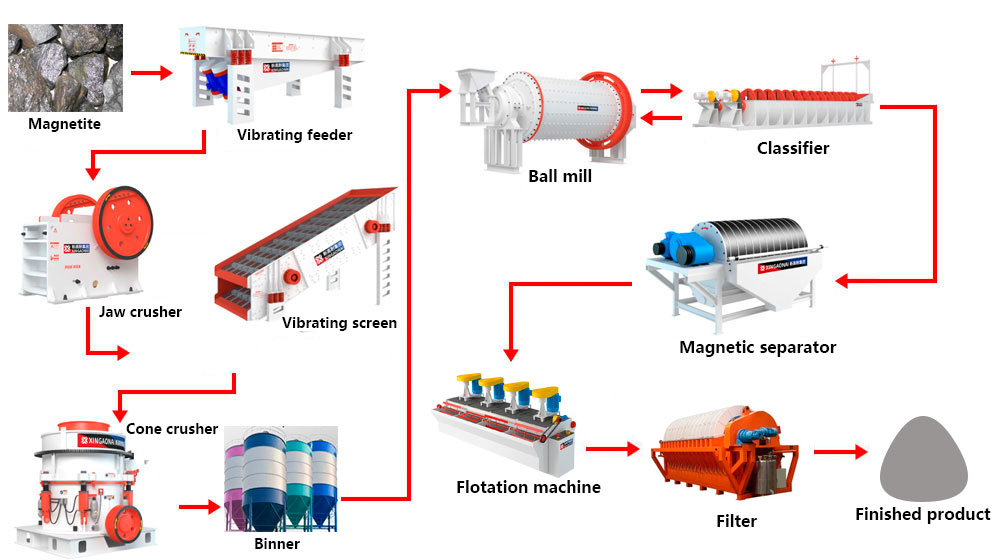
Magnetite beneficiation relies on the unique magnetic difference between magnetite and gangue minerals, with magnetic separation as the core process. The full workflow is optimized based on ore characteristics, typically including the following key stages:
1. Crushing & Grinding: Liberation of Magnetite Particles
Raw magnetite ore (large lumps of 0-1000mm) first undergoes crushing to reduce particle size:
Coarse Crushing: Jaw crushers break large ore into 100-200mm particles, ensuring uniform feeding for subsequent processing.
Fine Crushing: Cone crushers or impact crushers further reduce ore size to 10-20mm, preparing for grinding.
Grinding: Ball mills or rod mills grind crushed ore into slurry (particle size ≤0.074mm), fully liberating magnetite particles from gangue. A spiral classifier is used for grading—qualified slurry enters magnetic separation, while oversized particles are recycled for re-grinding.
2. Magnetic Separation: Core Stage of Magnetite Concentration
Magnetic separation leverages the strong magnetism of magnetite to separate it from non-magnetic gangue, with multi-stage separation adopted to ensure concentrate grade:
Rough Magnetic Separation: Wet magnetic separators (drum type is mainstream) remove most gangue minerals (quartz, feldspar) from the slurry, obtaining low-grade magnetite concentrate (iron grade 45-55%) and tailings.
Fine Magnetic Separation: The rough concentrate undergoes 1-3 stages of fine magnetic separation to further remove residual gangue. High-gradient magnetic separators are used for fine-grained magnetite, improving concentrate grade to 65-70% (meeting steelmaking requirements).
Sweeping Magnetic Separation: Tailings from rough separation are subjected to sweeping magnetic separation to recover residual magnetite particles, maximizing resource utilization and overall recovery rate (up to 95%+).
3. Separation of Magnetite from Key Associated Minerals
For magnetite ore with complex associated minerals, targeted auxiliary processes are added to ensure concentrate quality:
Magnetite & Hematite Separation: Hematite (weakly magnetic) is converted to magnetite via reduction roasting, then separated by magnetic separation.
Magnetite & Sulfide Separation: Flotation is used to remove sulfide minerals (pyrite, chalcopyrite) before magnetic separation—xanthate collectors are added to float sulfides, avoiding sulfur contamination of concentrate.
Magnetite & Apatite Separation: Anionic reverse flotation removes apatite (phosphorus-bearing mineral) from fine concentrate, reducing phosphorus content to meet high-quality steel standards (P ≤0.03%).
4. Dewatering & Storage
The final magnetite concentrate is dewatered via high-efficiency concentrators and filter presses (moisture content ≤10%), then stored or transported to steelmaking plants. The dewatered water is recycled to the grinding system, forming a closed-loop to save water and comply with environmental regulations.
Key Equipment Configuration for Magnetite Beneficiation Line
Our magnetite processing solution integrates high-efficiency, wear-resistant equipment tailored to the process requirements:
Crushing Equipment: Vibrating feeder (uniform feeding), jaw crusher (coarse crushing), cone crusher (fine crushing).
Grinding Equipment: Ball mill (primary grinding), rod mill (gentle grinding for fine particles), spiral classifier (grading).
Magnetic Separation Equipment: Wet drum magnetic separator (rough/fine separation), high-gradient magnetic separator (fine-grained magnetite), magnetic separator for sweeping.
Auxiliary Separation Equipment: Flotation machine (sulfide separation), reverse flotation cell (apatite removal), roasting furnace (hematite reduction).
Dewatering & Auxiliary Equipment: High-efficiency concentrator, filter press, reagent dosing system, dust removal equipment, closed-loop water circulation system.
Core Advantages of Our Magnetite Beneficiation Process
Targeting the characteristics of magnetite ore and steelmaking industry requirements, our solution offers distinct competitive edges:
High Efficiency & High Recovery: Optimized multi-stage magnetic separation process ensures concentrate grade ≥65% and recovery rate ≥95%, 10-15% higher than traditional processes.
Precise Impurity Removal: Targeted separation processes for associated minerals (sulfide, apatite, hematite) ensure concentrate meets steelmaking standards (low sulfur, low phosphorus).
Energy & Water Saving: Closed-loop water circulation system reduces water consumption by 60-70%; energy-efficient motors and optimized grinding parameters reduce power consumption by 12-18%.
Ore Adaptability: Custom process designs for different ore types (high-grade/low-grade magnetite, fine-grained/coarse-grained ore, complex associated ore) and production capacities (50-1000 TPH).
Environmental Compliance: Low-toxicity reagents, dust removal systems, and zero wastewater discharge meet global environmental regulations (CE, EPA, ISO 14001).
Cost-Effective Operation: Wear-resistant equipment components extend service life; automated reagent dosing and PLC control reduce labor costs and ensure stable operation.
Application Scenarios of Magnetite Beneficiation Solution
Our magnetite processing line is widely applied in global iron and steel industries and mineral processing sectors:
Steelmaking Industry: Supplies high-grade magnetite concentrate (Fe ≥65%) as the main raw material for blast furnaces and electric furnaces, reducing steelmaking energy consumption and improving steel quality.
Metallurgical Industry: Used for producing pig iron, cast iron, and alloy steel, leveraging the high iron content and low impurity of magnetite concentrate.
Mining Industry: Upgrades low-grade magnetite ore (Fe 20-35%) to high-grade concentrate for commercial sale, maximizing the value of magnetite resources.
Foundry Industry: Provides high-purity magnetite powder as a molding material, improving the surface quality and precision of castings.
Conclusion
Magnetite is an irreplaceable raw material for the global steel industry, and a professional magnetite beneficiation process is the key to unlocking its industrial value. Our solution, centered on high-efficiency magnetic separation and tailored to ore characteristics, delivers high-grade, low-impurity concentrate while ensuring energy conservation, environmental protection, and cost efficiency.