A linear vibrating screen is a versatile industrial screening equipment designed for efficient classification, grading, and sorting of bulk materials such as ores, aggregates, coal, and construction waste. As a key component in material processing lines, the linear vibrating screen uses high-frequency linear vibration to separate materials into different particle size grades, ensuring uniform product quality and improving downstream processing efficiency. Widely used in mining, metallurgy, construction, coal, and chemical industries, the linear vibrating screen is favored for its simple structure, high screening efficiency, and stable performance—making it an indispensable tool in modern material processing operations.
Unlike other screening equipment, the linear vibrating screen generates linear vibration through a vibration motor, which drives the screen surface to move in a straight line at a certain angle. This linear motion ensures that materials move forward evenly on the screen surface, maximizing contact with the screen mesh and improving screening accuracy. The linear vibrating screen can be customized with different screen mesh sizes and layers to meet diverse classification needs, from coarse grading to fine screening. Below is a comprehensive guide to the linear vibrating screen, covering its working principle, core features, types, applications, and maintenance best practices.
Working Principle of a Linear Vibrating Screen
The linear vibrating screen operates based on the principle of high-frequency linear vibration, driven by a dual-vibration motor or an eccentric shaft vibration device. The core mechanism is simple yet efficient, ensuring precise and uniform material classification:
The linear vibrating screen consists of a screen box, screen mesh, vibration motor, damping device, and frame. When the vibration motor starts, its two eccentric blocks rotate in opposite directions at the same speed, generating a resultant force that acts on the screen box in a linear direction. This force drives the screen box (and the screen mesh attached to it) to vibrate linearly at high frequency (typically 1500-3000 r/min) and a certain amplitude.
When bulk materials are fed onto the screen surface, the linear vibration causes the materials to move forward in a parabolic trajectory. During this movement, materials with particle sizes smaller than the screen mesh pass through the mesh (called undersize materials), while materials larger than the screen mesh remain on the screen surface (called oversize materials) and are discharged from the end of the screen. The amplitude and vibration frequency of the linear vibrating screen can be adjusted to control the movement speed of materials and the screening efficiency, adapting to different material characteristics and classification requirements.
Core Features of a Linear Vibrating Screen
The linear vibrating screen is distinguished by a set of core features that make it ideal for various material classification applications, balancing efficiency, versatility, and durability:
1. High Screening Efficiency
The linear vibration design of the linear vibrating screen ensures that materials move evenly and fully on the screen surface, maximizing the contact area between materials and the screen mesh. This reduces material blockage and improves screening efficiency—typically 85-95%, which is higher than other types of screening equipment. The high-frequency vibration also helps to break up agglomerated materials, further enhancing screening accuracy.
2. Precise Classification
The linear vibrating screen can be equipped with single or multiple screen layers (up to 4 layers) and different screen mesh sizes, enabling precise classification of materials into multiple particle size grades in one pass. The adjustable amplitude and vibration frequency allow operators to fine-tune the screening effect, ensuring that the final product meets strict quality standards for downstream applications.
3. Simple Structure & Easy Maintenance
The linear vibrating screen has a compact and simple structure, with fewer wearing parts. The screen mesh is easy to replace, and the vibration motor requires minimal maintenance—only regular lubrication and inspection. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs, ensuring long-term stable operation of the linear vibrating screen.
4. Strong Versatility
The linear vibrating screen can handle a wide range of materials, including dry materials, wet materials, and viscous materials (with appropriate adjustments). It is suitable for screening ores, aggregates, coal, sand, cement, chemical raw materials, and food processing materials, making it a versatile choice for various industries.
5. Low Noise & Stable Operation
Equipped with damping devices (such as rubber springs), the linear vibrating screen effectively reduces vibration transmission to the frame and surrounding equipment, minimizing operational noise. The vibration motor operates stably, with low energy consumption and long service life, ensuring reliable performance even in harsh industrial environments.
Common Types of Linear Vibrating Screens
Linear vibrating screens are available in various types, each designed for specific material characteristics, screening requirements, and industrial applications. The most common types include:
1. High-Efficiency Linear Vibrating Screen
The high-efficiency linear vibrating screen is the most widely used type, featuring a high vibration frequency, large amplitude, and steep screen angle. It is designed for high-volume material screening, with a screening efficiency of over 90%. This type of linear vibrating screen is suitable for mining, aggregate processing, and coal industries, where large quantities of materials need to be classified quickly.
2. Fine Linear Vibrating Screen
The fine linear vibrating screen is designed for fine screening applications, with a small amplitude, high vibration frequency, and dense screen mesh. It is used to separate fine particles (0.1-5mm) from materials, ensuring high screening accuracy. The fine linear vibrating screen is commonly used in cement plants, chemical industries, and powder processing facilities.
3. Wet Linear Vibrating Screen
The wet linear vibrating screen is equipped with a water spray device, which sprays water onto the screen surface during operation to wash away fine particles and prevent screen mesh blockage. It is suitable for screening wet, viscous materials such as clay, ore slime, and construction waste. The wet linear vibrating screen is widely used in mineral processing and aggregate washing plants.
4. Heavy-Duty Linear Vibrating Screen
The heavy-duty linear vibrating screen has a robust structure, thick screen box, and high-load-bearing capacity. It is designed for screening large, heavy materials such as large ores and bulky aggregates, with a feed size of up to 500mm. This type of linear vibrating screen is used in large-scale mining and construction projects, where durability and load-bearing capacity are critical.
Industrial Applications of Linear Vibrating Screens
Linear vibrating screens are widely used in industries that require efficient material classification, grading, and sorting. Their versatility and efficiency make them suitable for a range of applications, including:
1. Mining & Mineral Processing
In mining operations, linear vibrating screens are used to classify ores (such as gold, copper, iron, and limestone) after crushing. They separate ore particles into different grades, ensuring that only the appropriate particle size enters downstream equipment (such as ball mills and flotation machines) for mineral extraction. This improves processing efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
2. Aggregate Production
Aggregate plants rely on linear vibrating screens to grade aggregates (sand, gravel, and crushed stone) into different particle size grades for concrete, asphalt, and road construction. The linear vibrating screen ensures that the aggregates meet the strict quality standards for particle size distribution, improving the strength and durability of construction materials.
3. Coal Industry
In the coal industry, linear vibrating screens are used to screen coal into different grades (such as lump coal and powder coal) and remove impurities (such as gangue). This improves the quality of coal and ensures that it meets the requirements of different end-users, such as power plants and steel mills.
4. Cement & Building Materials Industry
Cement plants use linear vibrating screens to screen raw materials (limestone, clay, and gypsum) and finished cement products. The linear vibrating screen ensures uniform particle size distribution of raw materials, improving the efficiency of cement production, and classifies finished cement into different grades for various construction applications.
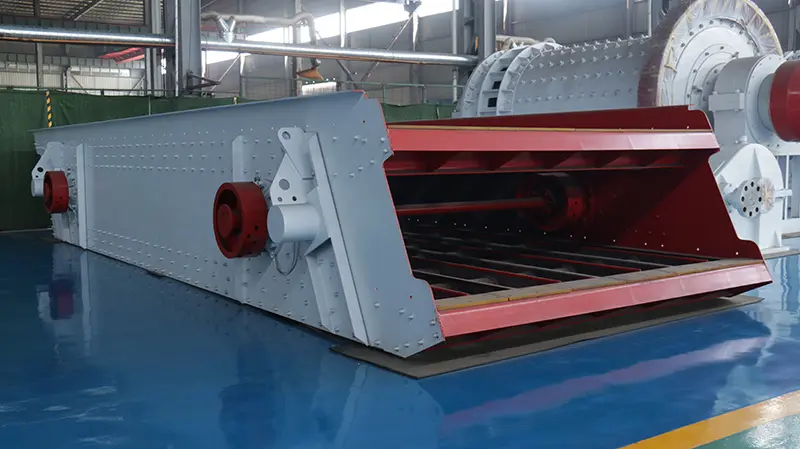

Maintenance Best Practices for Linear Vibrating Screens
Proper maintenance of a linear vibrating screen is essential to extend its service life, reduce downtime, and ensure optimal screening performance. Follow these maintenance best practices:
1. Regular Inspection
Conduct daily visual inspections of the linear vibrating screen to check for signs of wear, damage, or loose components. Inspect the screen mesh for tears, blockages, or excessive wear; check the vibration motor for leaks, abnormal noise, or overheating; and check the damping devices for damage or deformation. Conduct weekly detailed inspections to tighten loose bolts and check the lubrication system.
2. Lubrication
Keep the vibration motor’s bearings properly lubricated using the manufacturer-recommended lubricant. Regular lubrication reduces friction and wear, prevents overheating, and extends the service life of the motor. Check the lubricant level and quality daily, and replace the lubricant at the recommended intervals (typically every 3-6 months).
3. Screen Mesh Replacement
Replace the screen mesh promptly when it shows signs of tears, holes, or excessive wear. A damaged or worn screen mesh reduces screening accuracy and efficiency, and may cause material blockage. Choose the appropriate screen mesh size and material (such as stainless steel, manganese steel, or polyurethane) based on the material being screened.
4. Cleanliness
Keep the linear vibrating screen clean of material buildup, dust, and debris. Use a brush, air compressor, or low-pressure water to clean the screen surface, screen box, and discharge chute regularly. Buildup can cause blockages, reduce screening efficiency, and accelerate wear of components.
5. Proper Operation
Operate the linear vibrating screen within the manufacturer’s recommended parameters, including feed size, feed rate, and vibration frequency. Avoid overloading the screen, as this increases the load on the vibration motor and screen mesh, leading to premature wear. Ensure the feed material is evenly distributed on the screen surface to avoid uneven wear and poor screening results.
Conclusion
A linear vibrating screen is a vital piece of equipment in modern material processing lines, designed to deliver efficient, precise classification of bulk materials into different particle size grades. Its unique linear vibration principle, core features, and versatile types make it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, from mining and aggregate production to coal, cement, and food processing.
By understanding the working principle, types, applications, and maintenance requirements of a linear vibrating screen, you can choose the right equipment for your specific needs, extend its service life, and ensure optimal performance. Investing in a high-quality linear vibrating screen and following proper maintenance practices is essential to reducing operational costs, minimizing downtime, and maximizing the efficiency of your material processing operations—making it a valuable asset for any industrial operation requiring material classification.




