A vibrating feeder is a widely used piece of equipment in mining, metallurgy, construction, chemical processing, and manufacturing industries. Understanding the vibrating feeder working principle helps operators select the right equipment, optimize production efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs.
What Is a Vibrating Feeder?
A vibrating feeder is a mechanical device designed to transport bulk materials from a storage hopper or bin to downstream equipment, such as crushers, conveyors, or screens. It uses controlled vibration to move materials forward in a stable and continuous flow.
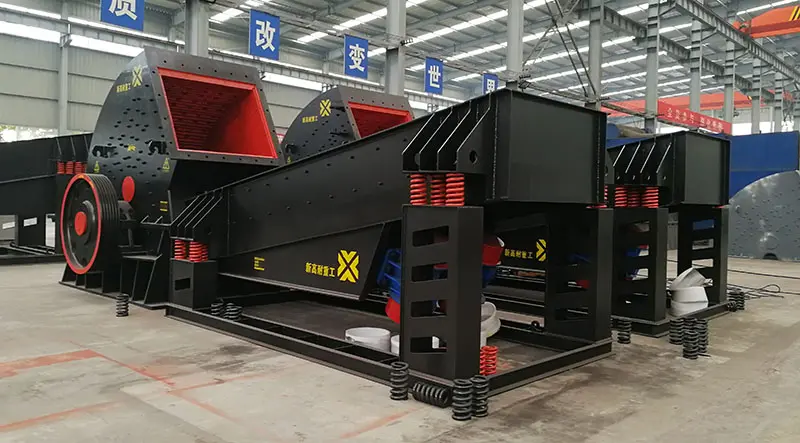

Vibrating Feeder Working Principle Explained
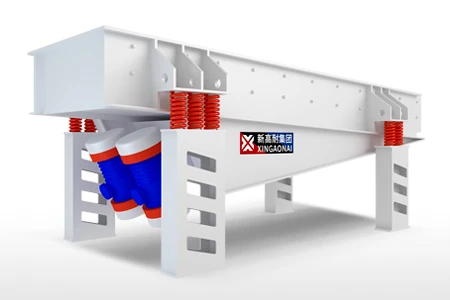
The vibrating feeder working principle is based on vibration generated by an excitation source, usually an electromagnetic drive or motor-driven eccentric shaft. When the feeder is activated, this excitation force causes the feeder trough to vibrate at a specific frequency and amplitude.
As the trough vibrates, the material placed on it experiences a combination of upward and forward motion. During the upward movement, friction between the material and the trough is reduced, allowing the material to momentarily lift or loosen. During the forward movement, the material advances along the trough. Repeating this motion rapidly results in a smooth, controlled, and continuous material flow.
Key Components Supporting the Working Principle
Several components work together to ensure the vibrating feeder operates efficiently:
Exciter or Motor: Generates the vibration force.
Feeder Trough: Holds and transports the material.
Springs or Rubber Mounts: Support the trough and absorb vibration.
Controller (for electromagnetic feeders): Adjusts vibration intensity and feed rate.
These components directly influence the vibrating feeder working principle by controlling vibration direction, frequency, and amplitude.
Advantages of the Vibrating Feeder Working Principle
The vibrating feeder working principle offers several practical advantages:
Uniform Feeding: Ensures consistent material flow.
Adjustable Feed Rate: Easy control by changing vibration parameters.
Low Energy Consumption: Efficient material movement with minimal power.
High Reliability: Simple structure with fewer wearing parts.
These benefits make vibrating feeders suitable for handling a wide range of materials, including powders, granules, and large bulk solids.
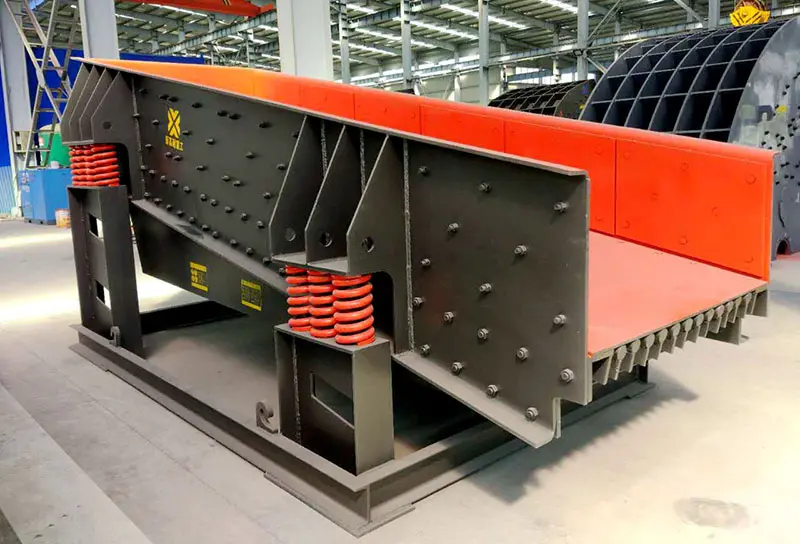

Applications of Vibrating Feeders
Due to the efficiency of the vibrating feeder working principle, these machines are commonly used in:
Mining and quarrying
Aggregate and sand production
Food and pharmaceutical processing
Recycling and waste management
Chemical and cement industries
Conclusion
The vibrating feeder working principle relies on controlled vibration to achieve efficient, stable, and continuous material transportation. By understanding how vibration frequency, amplitude, and direction affect material movement, industries can maximize productivity and equipment lifespan. Vibrating feeders remain an essential solution for modern bulk material handling systems.