In construction, aggregate production, and mining industries, clean sand with low impurity content is essential for ensuring the strength and durability of concrete, asphalt, and other building materials. A
wheel sand washing machine (also known as a wheel-type sand washer) is a specialized piece of equipment designed to remove dust, mud, and impurities from crushed sand, gravel, or natural sand—delivering high-purity, well-graded finished products. Below is a comprehensive guide to answering "what is a wheel sand washing machine" by exploring its definition, working principle, key components, features, applications, and advantages.
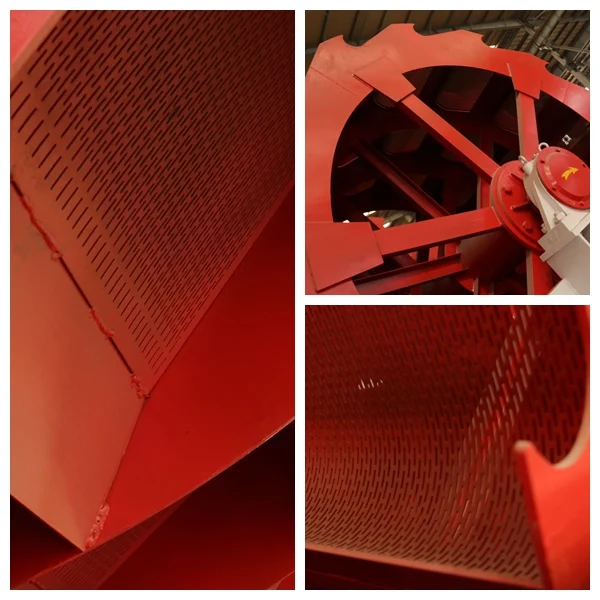
A wheel sand washing machine is a water-based cleaning equipment that uses mechanical force and water flow to separate impurities (such as dust, clay, and organic matter) from sand particles. It features a rotating wheel (or multiple wheels) with blades, which agitates and lifts sand in a water tank, allowing impurities to be washed away with the overflow water. Unlike other sand washing solutions (e.g., spiral sand washers), the wheel-type design prioritizes gentle cleaning—minimizing sand loss while ensuring thorough impurity removal. It is widely recognized for its simplicity, efficiency, and low maintenance, making it a staple in sand processing lines worldwide.
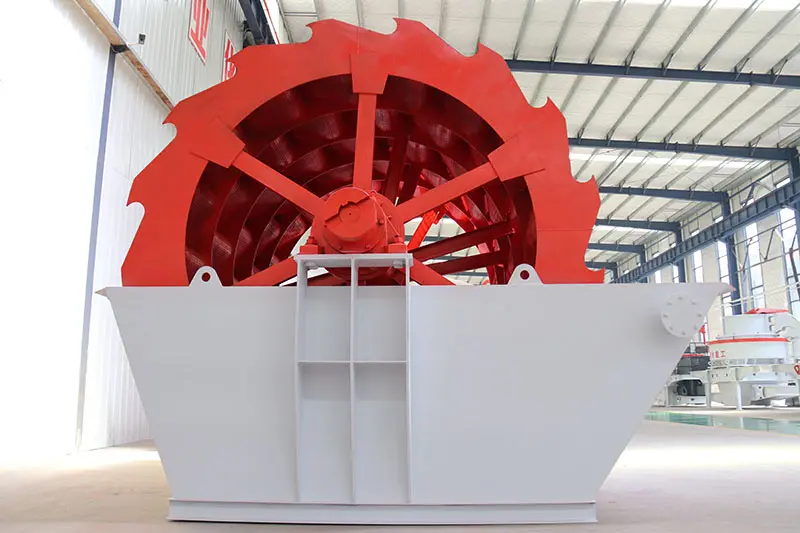

The operation of a wheel sand washing machine follows a straightforward, efficient process that combines mechanical agitation and hydraulic separation:
Feeding: Crushed sand or natural sand is transported to the machine’s water tank via a conveyor belt or feeder—ensuring uniform feeding to avoid overload.
Agitation & Cleaning: The motor drives the reducer, which rotates the wheel (equipped with high-strength blades) at a steady speed (typically 10-20 rpm). As the wheel rotates, the blades lift and stir the sand, creating friction between sand particles and washing away surface impurities (dust, mud).
Impurity Separation: Water is continuously injected into the tank, forming a stable water flow. Light impurities (e.g., dust, clay particles) are carried away by the overflow water and discharged through the drain pipe, while heavy sand particles remain in the tank.
Dehydration & Discharge: The rotating wheel lifts the cleaned sand out of the water tank. During the lifting process, excess water drains back into the tank, and the clean, dehydrated sand is discharged onto a conveyor belt for storage or further processing.
To understand "what is a
wheel sand washing machine" fully, it’s important to recognize its core components—each playing a critical role in performance:
Water Tank: A durable steel tank that holds water and sand during the cleaning process; designed with a sloped bottom to facilitate impurity discharge.
Rotating Wheel: The core working part, usually made of wear-resistant steel or rubber-lined blades to reduce sand loss and extend service life.
Motor & Reducer: Provide stable power for the wheel’s rotation; equipped with overload protection to prevent damage from excessive loads.
Feeding & Discharging System: Includes a feeding hopper and discharge chute to ensure smooth material flow in and out of the machine.
Water Supply & Drainage System: Controls water injection and overflow, maintaining optimal water level for effective cleaning.
What sets a wheel sand washing machine apart from other cleaning equipment? Its key features address the needs of sand processing lines:
Efficient Impurity Removal: Removes 95%+ of dust, mud, and organic impurities, producing sand that meets construction grade standards (e.g., GB/T 14684-2022).
Low Sand Loss: The gentle rotating wheel design minimizes sand particle breakage and loss—sand recovery rate exceeds 98%, reducing material waste.
Energy & Water Saving: Requires 20-30% less energy than spiral sand washers; supports recycled water use, lowering water consumption by up to 40%.
Durable & Low Maintenance: Wear-resistant components (e.g., rubber blades, steel tank) withstand abrasive materials; simple structure allows easy access for cleaning and part replacement.
Versatile Capacity: Available in single-wheel, double-wheel, or multi-wheel models, with processing capacities ranging from 10-300 t/h—suitable for small workshops to large-scale aggregate plants.
Now that we’ve answered "what is a wheel sand washing machine," let’s explore where it’s used. Its ability to produce clean sand makes it indispensable in:
Construction Industry: Cleaning sand for concrete, mortar, asphalt, and precast concrete components (e.g., blocks, pipes).
Aggregate Production: Processing crushed stone sand, river sand, and mountain sand for highway, bridge, and building projects.
Mining Industry: Cleaning mineral sand (e.g., quartz sand, feldspar sand) during beneficiation processes to improve mineral purity.
Glass & Ceramic Manufacturing: Producing high-purity sand for glass melting and ceramic raw material processing.
Water Conservancy Projects: Cleaning sand for dam construction, river dredging, and coastal reclamation.
Compared to alternative sand cleaning equipment (e.g., spiral sand washers, bucket sand washers), a
wheel sand washing machine offers distinct benefits:
Gentler Cleaning: Ideal for fragile sand particles (e.g., natural river sand) that require minimal breakage.
Simpler Operation: No complex internal structures—operators can master it with basic training.
Smaller Footprint: Compact design saves workshop space, making it suitable for limited-area sites.
Lower Operating Costs: Reduced energy, water, and maintenance expenses translate to higher profit margins for users.




