In the crushing industry, the construction of jaw crusher directly determines its performance, durability, and operational efficiency. A well-designed crusher structure ensures stable material reduction, low maintenance costs, and long service life—critical for mining, construction, and aggregate production projects. This article breaks down the core components, design principles, and assembly workflows of jaw crusher construction, while highlighting how structural optimization enhances overall equipment reliability.
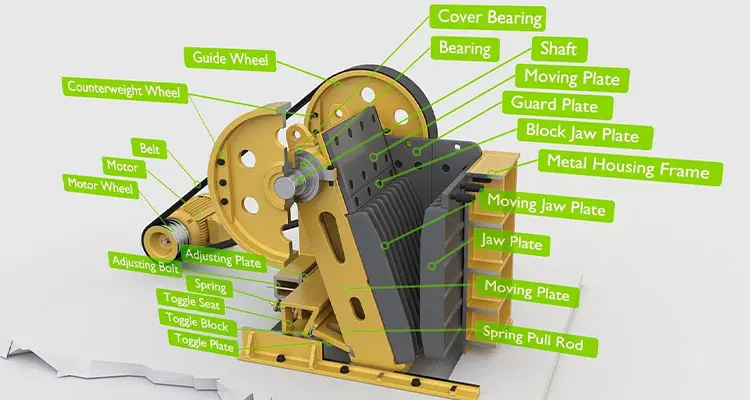
Core Components in the Construction of Jaw Crusher
1. Frame Structure
Cast Steel Frame: Made from high-grade cast steel (e.g., ZG270-500), it offers exceptional rigidity and impact resistance, ideal for heavy-duty industrial jaw crushers used in mining. Its one-piece casting eliminates welding seams, reducing the risk of structural failure under high loads.
Welded Steel Frame: Constructed from thick steel plates welded together, it is lighter and more cost-effective, suitable for small to medium-sized jaw crushers for construction waste recycling. Advanced welding techniques ensure the frame maintains structural integrity during long-term operation.
2. Jaw Plate Assembly
Fixed Jaw Plate: Bolted firmly to the frame’s front wall, its surface features a serrated or wave-shaped profile to enhance material grip during crushing. In high-quality jaw crusher construction, fixed jaw plates are made from manganese steel (Mn13 or Mn18) for superior wear resistance.
Movable Jaw Plate: Attached to the movable jaw body, it moves reciprocally to squeeze materials against the fixed jaw. The construction of the movable jaw plate often incorporates heat treatment (quenching and tempering) to extend its service life by 20–30% compared to standard steel plates.
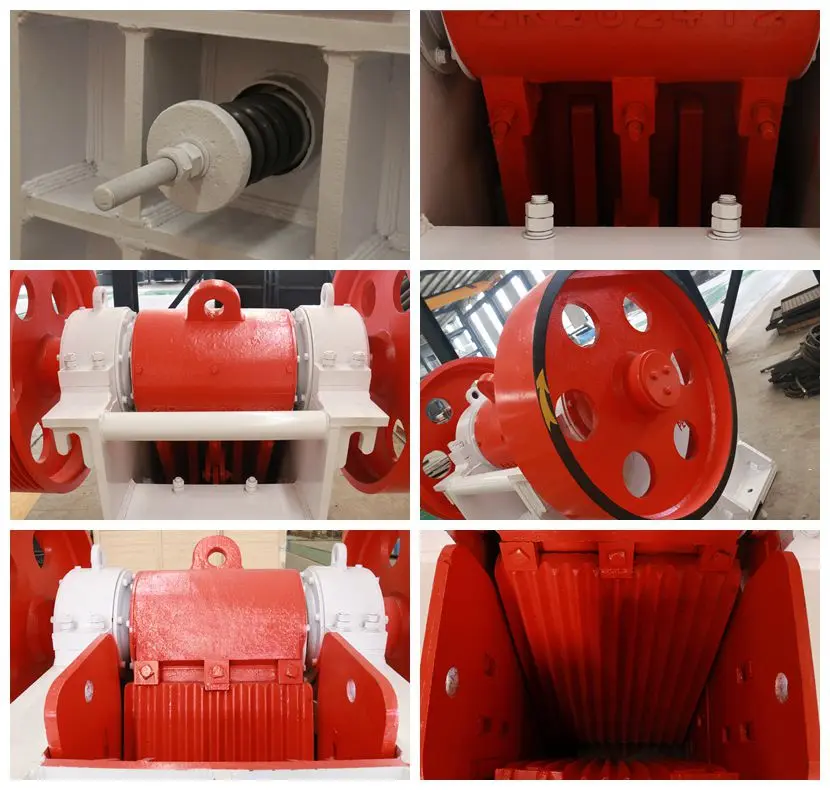
3. Eccentric Shaft and Transmission System
Material: Forged from high-strength alloy steel (e.g., 40CrNiMoA) to withstand torque and fatigue, with precision machining to ensure smooth rotation.
Transmission Matching: In typical jaw crusher construction, the shaft connects to a motor via a V-belt and reducer, with a flywheel attached to one end to balance load and reduce vibration during operation.
4. Toggle Plate and Adjustment Mechanism
Design Principles Guiding the Construction of Jaw Crusher
Rigidity and Load Distribution: All components in the construction of jaw crusher are engineered to evenly distribute crushing forces (which can exceed 100 tons for large models), preventing localized stress that causes premature wear or failure.
Wear Resistance: Critical parts (jaw plates, eccentric shaft bushings) use high-wear materials, and the construction of jaw crusher incorporates replaceable wear parts to minimize downtime for maintenance.
Safety and Accessibility: The construction of jaw crusher includes protective covers for rotating components (eccentric shaft, belt drive) and easy-to-access hatches for replacing jaw plates, ensuring operator safety and simplifying routine upkeep.
Assembly Workflow for the Construction of Jaw Crusher
Frame Preparation: The frame is cleaned and inspected for defects (e.g., cracks in cast frames or welding flaws in welded frames). Machining is done to ensure mounting surfaces for components are level and aligned.
Core Component Installation: The eccentric shaft is fitted into the frame’s bearing seats, followed by the movable jaw body and toggle plate. Bearings are lubricated with high-temperature grease to reduce friction during operation.
Jaw Plate Mounting: Fixed and movable jaw plates are bolted in place, with gaskets used to ensure a tight, vibration-free fit. The plate alignment is checked to avoid uneven wear during crushing.
Transmission and Safety Assembly: The motor, reducer, and V-belt are installed, and safety guards are attached to rotating parts. The discharge port is calibrated to meet the required particle size specifications.
Testing and Calibration: After assembly, the construction of jaw crusher concludes with a no-load test (to check for abnormal noise or vibration) and a load test (to verify crushing efficiency and product quality).

Trends in Modern Construction of Jaw Crusher
Modular Construction: Modern jaw crusher construction uses pre-assembled modules (frame, jaw assembly, transmission) to reduce on-site installation time by 40% and simplify transportation to remote mining sites.
Intelligent Integration: The construction of jaw crusher now includes sensors (vibration, temperature) embedded in key components, enabling real-time monitoring of structural health and preventing unplanned downtime.
Eco-Friendly Design: The construction of jaw crusher incorporates dust-sealing systems around the crushing chamber and noise-dampening materials in the frame, meeting strict environmental standards for urban construction projects.



