Core Components of a Jaw Crusher
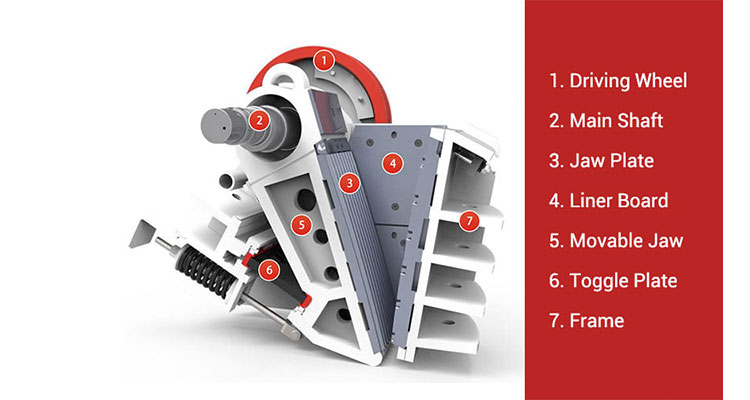
Fixed Jaw Plate: A stationary component attached to the heavy-duty frame, lined with wear-resistant material to withstand high pressure and friction from hard materials.
Movable Jaw Plate: The swinging component that interacts with the fixed jaw plate to apply compressive force. It is connected to the eccentric shaft and toggle plate, driving its reciprocating motion.
Eccentric Shaft: The power transmission core, driven by the motor. It converts rotational motion into the reciprocating swing of the movable jaw plate.
Toggle Plate: Acts as a connecting rod and safety component. It transmits force from the eccentric shaft to the movable jaw and protects the machine from overload by breaking under extreme pressure.
Feeding Hopper & Discharge Adjustment Device: The hopper ensures uniform feeding of large materials, while the discharge adjustment device (commonly wedge-type) controls the final product particle size by adjusting the gap between the two jaw plates.
How Jaw Crusher Works: Operating Principle
Step 1: Power Transmission & Movable Jaw Activation
Step 2: Material Feeding & Crushing Process
Step 3: Particle Size Control & Discharge
Optimized Design for Enhanced Performance

Key Factors Affecting How Jaw Crusher Works Efficiently
Material Properties: Hardness, humidity, and particle size of raw materials affect crushing efficiency. Jaw crushers are designed for hard and medium-hard materials, but excessively wet materials may cause blockages.
Feeding Uniformity: Uneven feeding leads to uneven wear of jaw plates and reduced efficiency. Ensure consistent feeding to keep the crushing chamber moderately filled.
Discharge Gap Setting: Incorrect gap settings result in uneven particle size or reduced throughput. Calibrate the gap according to production requirements using the wedge adjustment system.
Lubrication & Maintenance: Proper lubrication of the eccentric shaft and toggle plate ensures smooth motion. Regularly inspect and replace worn jaw plates to maintain crushing performance.
Common Issues in How Jaw Crusher Works & Troubleshooting
Low Crushing Efficiency: Cause: Insufficient motor power, worn jaw plates, or incorrect discharge gap. Solution: Check motor operation, replace worn parts, and recalibrate the discharge gap.
Uneven Discharge Particle Size: Cause: Uneven jaw plate wear or uneven feeding. Solution: Rotate or replace jaw plates, and optimize feeding uniformity.
Movable Jaw Jammed: Cause: Oversized materials or foreign objects entering the chamber. Solution: Stop the machine, clear the blockage, and check the feeding size.



